

Next: Restricted Open-Shell Hartree-Fock References
Up: CIS Energy Equations
Previous: Restricted Hartree-Fock References
Now consider the case when
 is obtained by the UHF
procedure. Once again, the Fock matrix is diagonal:
is obtained by the UHF
procedure. Once again, the Fock matrix is diagonal:
 .
However, it is customary to split the Fock
matrix into two matrices, one for
.
However, it is customary to split the Fock
matrix into two matrices, one for 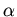 and one for
and one for 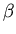 spin
orbitals (mixed terms such as
spin
orbitals (mixed terms such as
 and
and
 are zero). As for the RHF case,
are zero). As for the RHF case,
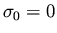 and
and
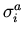 can be written
can be written
 |
(37) |
Unfortunately, for a UHF reference equations
(26)-(28) no longer hold, so that the
above equation can be simplified only to
 |
(38) |
Even though spin has been integrated out, the overbars must be kept in
the above equation because the spatial parts of spin orbitals i and
 are not necessarily equal. An analogous equation holds
for
are not necessarily equal. An analogous equation holds
for
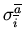 ,
,
![\begin{displaymath}\sigma_{\overline{i}}^{\overline{a}} = c_{\overline{i}}^{\ove...
...{i}) ]
+ \sum_{jb} c_j^b (\overline{a}\overline{i} \vert jb),
\end{displaymath}](img96.png) |
(39) |
and there is no general relationship between
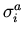 and
and
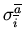 .
The pseudodensity matrices
.
The pseudodensity matrices
 and
and
 are defined as in eq. (31) and
(32), but they are no longer simply related.
Thus it is necessary to compute two Fock-like matrices, according to
are defined as in eq. (31) and
(32), but they are no longer simply related.
Thus it is necessary to compute two Fock-like matrices, according to
In contrast to RCIS, there are no longer separate singlet and triplet
cases, since the UCIS eigenfunctions are not CSFs. After transforming
to the MO basis by
the expressions for
 become
become


Next: Restricted Open-Shell Hartree-Fock References
Up: CIS Energy Equations
Previous: Restricted Hartree-Fock References
C. David Sherrill
2000-04-18



![\begin{displaymath}\sigma_{\overline{i}}^{\overline{a}} = c_{\overline{i}}^{\ove...
...{i}) ]
+ \sum_{jb} c_j^b (\overline{a}\overline{i} \vert jb),
\end{displaymath}](img96.png)



